Crypto enthusiasts looking to generate passive income often choose between two popular methods: staking and mining. While both options reward participants for supporting blockchain networks, they differ significantly in mechanics, costs, and environmental impact. This guide compares crypto staking and mining to help you determine which approach aligns with your financial goals and resources.
Understanding Crypto Mining
What Is Mining?
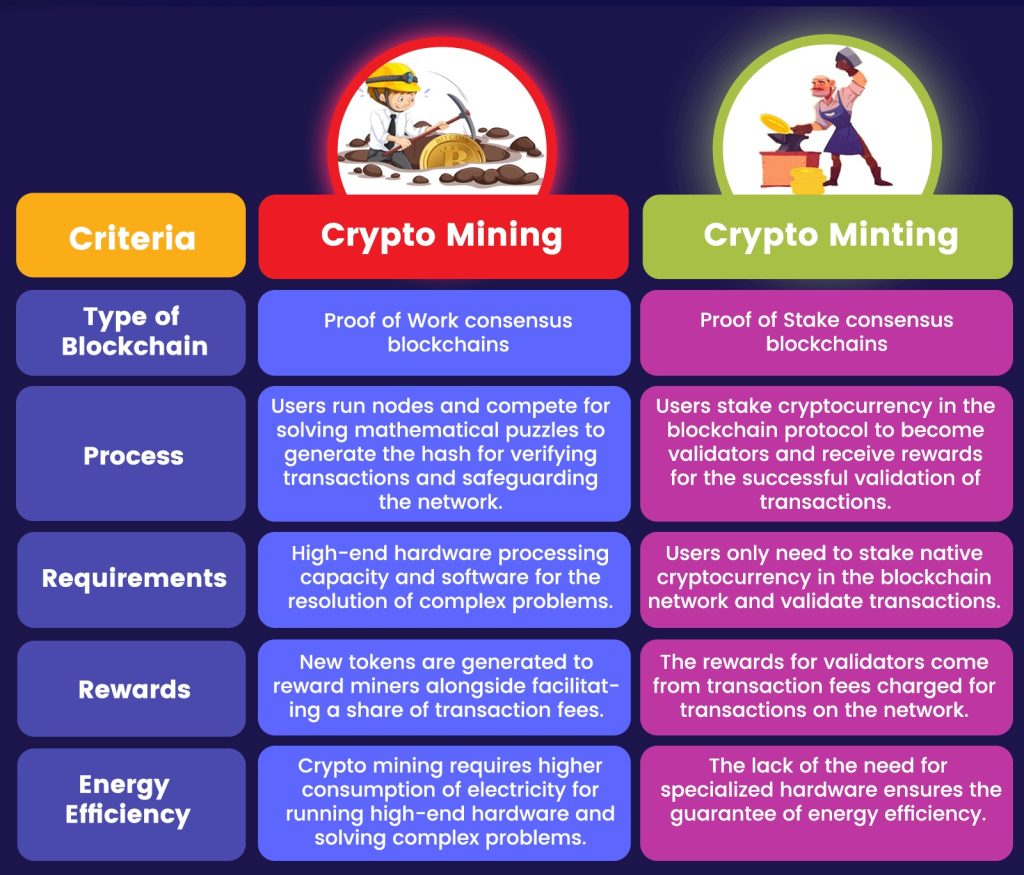
Mining is the process of validating transactions on Proof of Work (PoW) blockchains like Bitcoin. It involves solving complex mathematical puzzles using powerful hardware, such as ASICs or GPUs, to secure the network and create new coins. Miners earn rewards in the form of cryptocurrency and transaction fees.
Benefits of Mining
- High Potential Rewards: Miners often benefit significantly, particularly when participating in less competitive networks or early stages of a cryptocurrency’s lifecycle.
- Liquidity: Mined tokens are immediately accessible for trading or holding without lock-up periods.
- Network Contribution: Mining ensures blockchain security and decentralization.
Drawbacks of Mining
- High Costs: Mining requires expensive hardware and substantial electricity, making it resource-intensive.
- Environmental Impact: Energy-intensive processes contribute to large carbon footprints, raising sustainability concerns.
- Technical Expertise: Successful mining requires technical skills to maintain rigs and optimize operations.
Mining Profitability in 2024
Mining remains profitable for those with access to cheap electricity and efficient hardware. However, regulatory pressures and environmental concerns are shifting attention toward alternative methods like staking.

Understanding Crypto Staking
What Is Staking?
Staking operates on Proof of Stake (PoS) blockchains like Ethereum, Cardano, and Polkadot. Participants lock a certain amount of cryptocurrency in a wallet to validate transactions and secure the network. Stakers are rewarded with additional tokens proportional to their holdings and contribution.
Benefits of Staking
- Energy Efficiency: Unlike mining, staking does not require intensive energy consumption, making it environmentally friendly.
- Lower Entry Costs: Staking involves holding cryptocurrency instead of investing in hardware, reducing upfront costs.
- Predictable Rewards: Rewards from staking are consistent, depending on the amount staked and the network’s policies.
Drawbacks of Staking
- Locked Funds: Staked tokens are often inaccessible during lock-up periods, reducing liquidity.
- Network Risks: Issues like network downtime or attacks can impact rewards and even result in penalties.
- Centralization Concerns: Networks where wealthier participants dominate staking can lead to reduced decentralization.
Staking Profitability in 2024
Staking has become increasingly profitable, with many networks offering annual yields between 5% and 20%. Popular options like Ethereum 2.0 and Cardano attract long-term investors due to their stability and community support.
Comparing Mining and Staking
Costs and Barriers to Entry
- Mining: High startup costs due to hardware and energy needs.
- Staking: Lower costs; requires purchasing tokens but no hardware investment.
Environmental Impact
- Mining: Significant energy consumption contributes to environmental concerns.
- Staking: A greener alternative, consuming minimal energy.
Risk and Liquidity
- Mining: Hardware failure, rising electricity costs, and market fluctuations pose risks. However, mined tokens are liquid.
- Staking: Risks include lock-up periods and potential penalties for network issues, but it is less operationally intensive.
Profit Potential
- Mining: Higher rewards possible in certain conditions but dependent on market prices and competition.
- Staking: Predictable income streams with steady yields over time.

Which Is Better for Passive Income?
The choice between staking and mining depends on individual goals, resources, and environmental considerations.
- Choose Mining If: You have access to low-cost electricity, can invest in powerful hardware, and possess the technical expertise to maintain rigs. Mining may yield higher rewards, particularly for early adopters or in regions with cheap energy.
- Choose Staking If: You prefer a low-maintenance, environmentally friendly option with consistent returns. Staking suits those without the resources to manage hardware or those looking for a hands-off approach.
Final Thoughts
Both staking and mining offer opportunities to earn passive income, but they cater to different types of investors. While mining remains lucrative for those with the necessary resources, staking provides a more accessible and sustainable alternative.
Before committing, assess your financial capacity, technical skills, and risk tolerance. Diversifying your investments between staking and mining can also help balance rewards and mitigate risks in the dynamic world of cryptocurrency.







