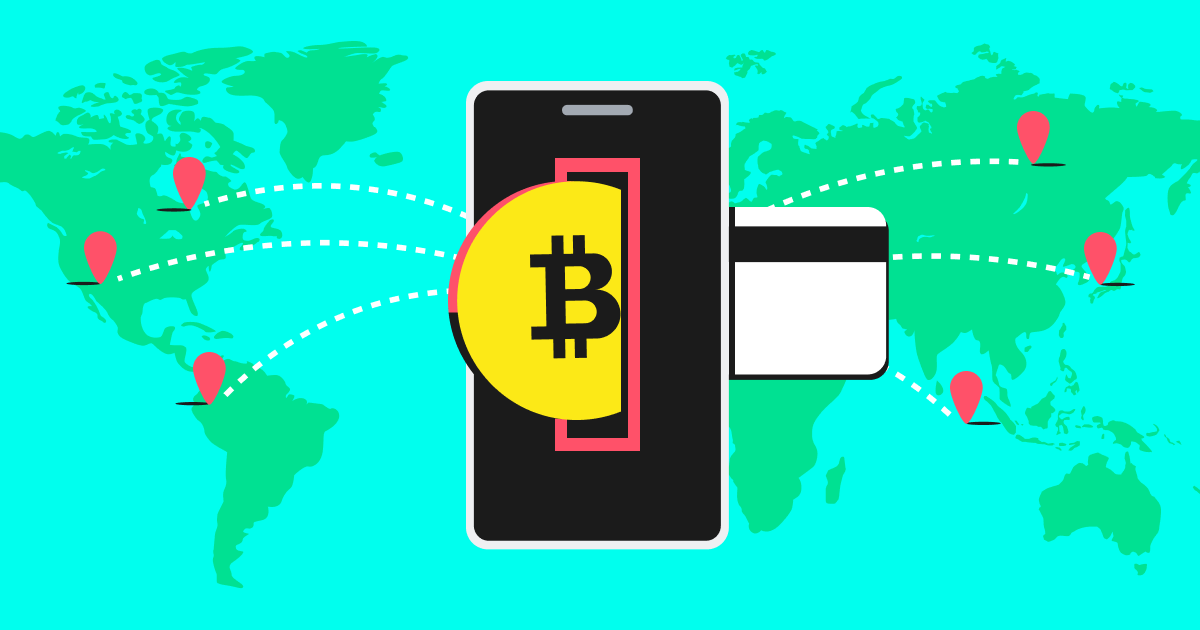
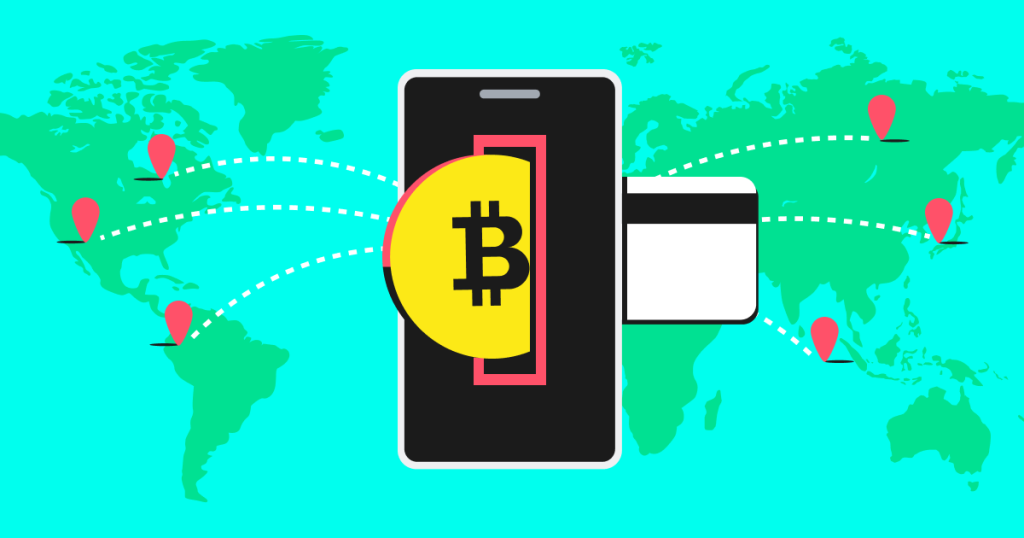
Cross-border payments, essential for global trade and remittances, have long been plagued by inefficiencies such as high costs, slow processing times, and lack of transparency. Cryptocurrency is revolutionizing this space by offering faster, cheaper, and more accessible alternatives to traditional systems. As the world embraces digital solutions, cryptocurrencies are poised to transform cross-border transactions fundamentally.

The Inefficiencies of Traditional Cross-Border Payments
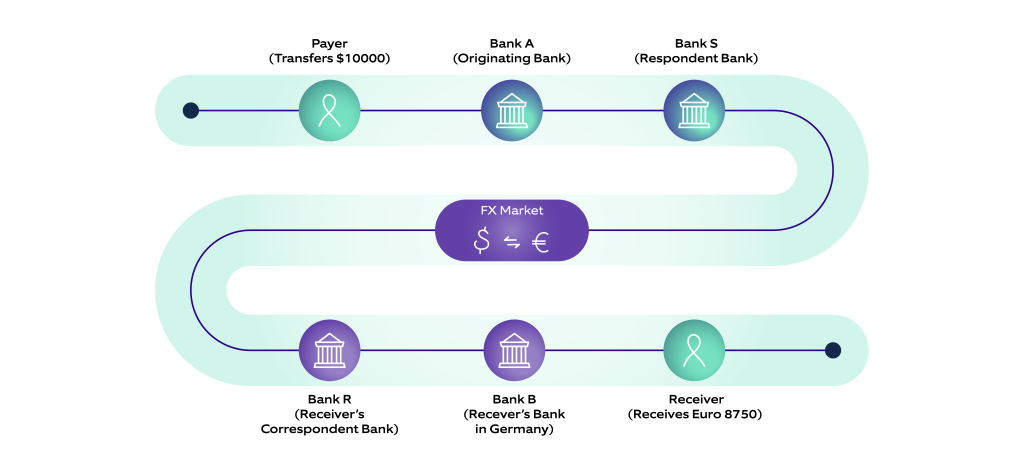
Traditional cross-border payments rely on a network of correspondent banks and financial institutions. These systems involve multiple intermediaries, increasing transaction costs and delays. A typical wire transfer can take 2–5 days to settle and cost up to $50 per transaction. Moreover, processes like currency conversion add complexity and unpredictability. For businesses and individuals, these inefficiencies hinder trade and financial inclusion, particularly in developing regions.
How Cryptocurrency Enhances Cross-Border Payments
1. Faster Transactions
Cryptocurrencies operate on blockchain technology, a distributed ledger that processes transactions almost instantly. Unlike traditional systems that rely on banking hours and multiple intermediaries, blockchain networks run 24/7. For instance, Bitcoin and Ethereum can complete cross-border transfers in minutes, while traditional wire transfers can take several days. This speed is especially beneficial for time-sensitive transactions like emergency remittances.
2. Lower Costs
Cryptocurrency transactions eliminate the need for intermediaries, significantly reducing fees. While traditional cross-border payments may incur costs ranging from 6% to 10% of the transaction amount, cryptocurrency transfers often cost just a fraction of that, especially when using stablecoins like USDT. These lower fees benefit small businesses and individuals who rely on remittances, freeing up more funds for productive use.
3. Increased Transparency
Blockchain technology ensures that all transactions are recorded on a public ledger, enhancing transparency. This transparency reduces fraud and disputes, as all parties can independently verify transaction details. For cross-border trade, this creates a more trustworthy and efficient ecosystem.
4. Financial Inclusion
Cryptocurrency provides a lifeline for the unbanked and underbanked populations. With only a smartphone and internet access, individuals can send and receive money globally without needing a traditional bank account. This democratization of financial services empowers people in developing countries to participate in the global economy.
5. Stability Through Stablecoins
Volatility has been a significant concern with cryptocurrencies, but stablecoins like USDC and DAI address this issue. These assets are pegged to fiat currencies, providing the stability needed for everyday transactions while retaining the benefits of blockchain technology.

Challenges and Considerations
1. Scalability
As blockchain networks handle more transactions, they face congestion and higher fees, particularly during peak times. Solutions like Layer 2 technologies and sharding aim to address these issues, but widespread implementation remains a challenge.
2. Regulatory Hurdles
Cryptocurrency adoption in cross-border payments is hindered by inconsistent regulations across countries. While some nations embrace crypto-friendly policies, others impose strict controls or outright bans. Global regulatory frameworks are needed to ensure seamless and legal use of cryptocurrencies.
3. Technological Literacy
Many potential users are unfamiliar with blockchain and cryptocurrencies, limiting adoption. Educational initiatives from crypto companies and governments can help bridge this knowledge gap and increase confidence in using digital assets.
Real-World Applications
- Remittances: Cryptocurrencies provide faster and cheaper alternatives for sending money home, especially for workers in foreign countries.
- Trade Settlements: Businesses can use cryptocurrencies to bypass currency conversion fees and delays, enabling smoother international trade.
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): Platforms like Ripple and Stellar enable seamless cross-border transactions, leveraging blockchain’s efficiency and scalability.
Final Thoughts
Cryptocurrency is revolutionizing cross-border payments by addressing the inefficiencies of traditional systems. Faster transactions, lower fees, and increased accessibility make digital currencies an attractive solution for global money transfers. However, challenges like scalability and regulation need to be addressed for mass adoption.
As blockchain technology matures, its transformative potential in cross-border payments could pave the way for a more inclusive and efficient global financial ecosystem. Whether for individuals sending remittances or businesses engaging in international trade, cryptocurrency offers a promising glimpse into the future of finance.








